Closure
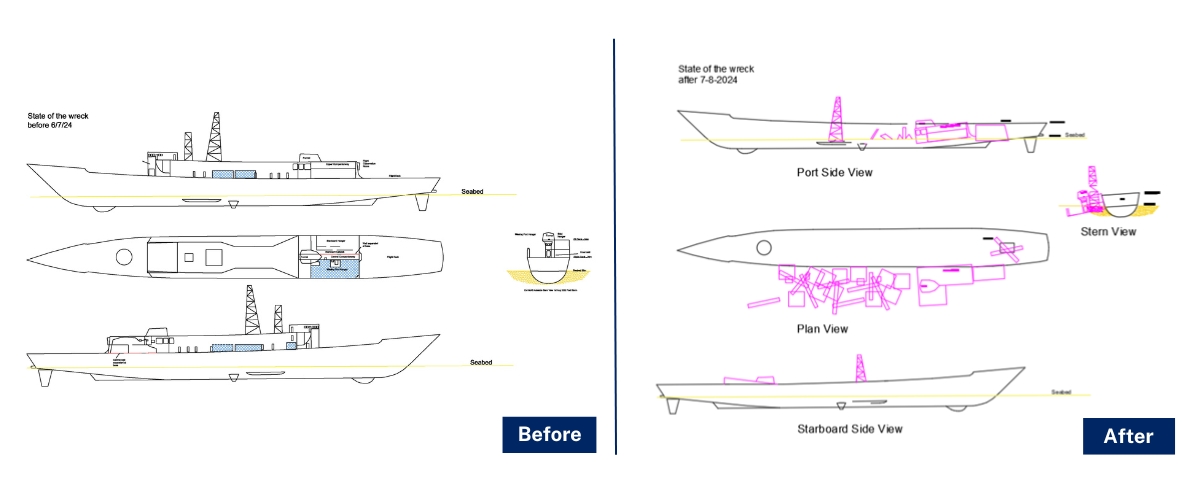
The dive site was closed in July 2024 due to structural damage caused during storm events. Mooring buoys were also removed due to public safety concerns.
A Structural Condition Report (PDF, 1.3 MB) in November 2024 confirmed that additional significant deterioration had occurred to the Ex-HMAS Adelaide since the closure. This includes the complete detachment and collapse of the aluminium superstructure from the hull.
Ongoing corrosion and further storms in January 2025 are expected to have caused additional movement and deterioration of the dive site. The Department commissioned a further Structural Condition Report of the dive site in March 2025.
Risks
The current condition of the wreck poses considerable risks to divers. Identified hazards include:
- Entrapment risks from collapsed passageways and blocked entry/exit points.
- Guillotine and crush hazards from jagged aluminium panels, shifting debris and collapsed sections moving in swells and currents.
- Increased diving depth to the wreck, increasing the risk of decompression sickness.
The public should not attempt to dive at the site. The two yellow special navigational markers were displaced during the storms and are no longer in their original positions.
Next steps
- In March 2025 the Department engaged a contractor to undertake a Structural Condition Report of the dive site. This will assess the impacts of the January 2025 storms and investigate the ongoing deterioration of the wreck.
- Once the structural condition report has been received and all relevant information has been considered, the Department will discuss the future management of the site with the Federal Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water (DCCEEW).
- Due to safety concerns, the dive site remains closed.
Background
The ex-HMAS Adelaide, an Oliver Perry-class frigate and former Royal Australian Navy warship was scuttled (sunk) in 2011 to create an artificial reef for marine life and the enjoyment of divers.
Located about 1.8 km off Avoca Beach, near Terrigal on the Central Coast of New South Wales, the ship lies at a depth of approximately 32 metres.
Artificial reefs, like the ex-HMAS Adelaide, are regulated under Commonwealth law to ensure they do not pose a significant threat to the marine environment or public safety.
Keeping up to date with our work
We will update this page as the project progresses.
Location image
About artificial reefs
The ex-HMAS Adelaide was prepared and sunk to create an artificial dive reef.
An artificial reef is a structure placed on the sea floor to attract new marine life to an area. These structures may improve fishing opportunities, serve as dive sites, help protect the coast , deter trawling activity, and reverse habitat loss.
The reef develops over time. It goes through various stages of marine growth and occupation, eventually becoming home to a thriving marine ecosystem that attracts divers from all over the world.
Environmental monitoring and reporting
Australian law regulates the creation of artificial reefs under the Environment Protection (Sea Dumping) Act 1981 (Commonwealth).
A sea dumping permit ensures that creating an artificial reef does not threaten the marine environment or marine users. After a comprehensive environmental assessment, a permit was issued for scuttling (sinking) the ex-HMAS Adelaide.
The Administrative Appeals Tribunal considered a wide range of environmental issues when it reviewed the permit and allowed the scuttling to go ahead.
An ongoing condition of the permit is that the department must monitor and report on the artificial reef, in keeping with a long-term monitoring and management plan . All results of this monitoring are available below.
In 2016, the ecological monitoring done in the 5 years since the scuttling was reviewed.
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Review of Environmental Factors report. (PDF, 13.4 MB)
- Sea Dumping Permit (PDF, 663 KB)
- Administrative Appeals Tribunal decision (PDF, 403 KB)
- Administrative Appeals Tribunal decision plain English summary (PDF, 179 KB)
- Long-Term Monitoring and Management Plan 2018 version (PDF, 7.5 MB)
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide 5-year review of ecological monitoring (PDF, 3.3 MB)
- Environmental Monitoring - Sediment Quality, Bioaccumulation + Invasive Pests (PDF, 1.3 MB)
Post-scuttling report April 2011
This report confirms the date and time of placement, position, water depth, inspection dives and position of navigation markers.
Additional surveys and reports
These reports describe the development of the reef community.
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Baseline Survey (PDF, 5.6 MB) sampled April 2011
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Survey 1 (PDF, 2.7 MB) sampled October 2011
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Survey 2 (PDF, 3.6 MB) sampled February 2012
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Survey 3 (PDF, 6.7 MB) sampled May 2012
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Survey 4 (PDF, 11.2 MB) sampled July 2012
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Survey 5 (PDF, 7.2 MB) sampled October 2012
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Survey 6 (PDF, 11 MB) sampled January 2013
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Survey 7 (PDF, 13.5 MB) sampled April 2013
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Survey 8 (PDF, 15.6 MB) sampled July 2013
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Survey 9 (PDF, 23.9 MB) sampled October 2013
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Survey 10 (PDF, 17.4 MB) sampled March 2014
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Survey 11 (PDF, 1.6 MB) sampled September 2014
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Survey 12 (PDF, 20.2 MB) sampled March 2015
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef Community Monitoring Survey 13 (PDF, 11.9 MB) sampled June 2016
These reports monitor seabed sediment quality and movement, including how metal corrosion and paint degradation could potentially influence the surrounding environment.
- Ex-HMAS Adelaide Artificial Reef - Marine Sediment Quality Report (PDF, 3.3 MB) sampled May 2011
- Sediment Quality Monitoring Survey 1 (PDF, 1.5 MB) sampled October 2011
- Sediment Quality Monitoring Survey 2 (PDF, 1.4 MB) sampled January 2013
- Sediment Quality Monitoring Survey 3 (PDF, 1.7 MB) sampled June 2016
Bioaccumulation monitoring determines if resident marine species are likely to be affected by the vessel’s zinc chromate paint.
- Bioaccumulation Study (PDF, 1.6 MB) sampled May 2011
- Bioaccumulation Monitoring Survey 1 (PDF, 1.3 MB) sampled Jan 2012
Regular structural inspections and assessments of the ship are conducted in line with the long-term monitoring and management plan.
Download the Structural Condition Report (1.28 MB) published November 2024.
Qualified commercial divers regularly inspect the ex-HMAS Adelaide and report on the condition of the wreck.
- Structural Monitoring – Diver’s Report – June 2015 (PDF, 1.7 MB)
- Structural Monitoring – Diver’s Report – April 2017 (PDF, 13.2 MB)
- Structural Monitoring – Diver’s Report – July 2018 (PDF, 3.7 MB)
- Structural Monitoring – Diver’s Report – June 2019 (PDF, 5.9 MB)
- Structural Monitoring – Diver's Report – March 2020 (PDF, 8.3 MB)
- Structural Monitoring – Diver's Report – April 2021 (PDF, 5.8 MB)
- Structural Monitoring – Diver's Report – July 2021 (PDF, 4.3 MB)
- Structural Monitoring – Diver's Report – June 2022 (PDF, 4 MB)
- Structural Monitoring – Diver's Report – August 2022 (PDF, 1,356 KB)
- Structural Monitoring – Diver's Report – June 2023 (PDF, 3.3 MB)
- Diver's Report – Ex HMAS Adelaide Panel Removal - October 2023 (PDF 1.1 MB)
Marine engineers review the divers’ reports, assess the condition of the wreck and identify any factors that may require ongoing monitoring.
- Structural Monitoring – Engineer’s Report – April 2015 (PDF, 165 KB)
- Structural Monitoring – Engineer’s Report – April 2017 (PDF, 132 KB)
- Structural Monitoring – Engineer’s Report – April 2018 (PDF, 121 KB)
- Structural Monitoring – Engineer’s Report – June 2019 (PDF, 118 KB)
- Structural Monitoring – Engineer's Report – March 2020 (PDF, 123 KB)
- Structural Monitoring – Engineer's Report – June 2021 (PDF, 123 KB)
- Structural Monitoring – Engineer's Report – June 2022 (PDF, 118 KB)
- Structural Monitoring – Engineer's Report – August 2022 (PDF, 119 KB)
- Structural Monitoring – Engineer's Report – July 2023 (PDF, 128 KB)